|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Acceptability of clinical decision support prototypes for a nursing electronic health record to facilitate palliative care outcomes.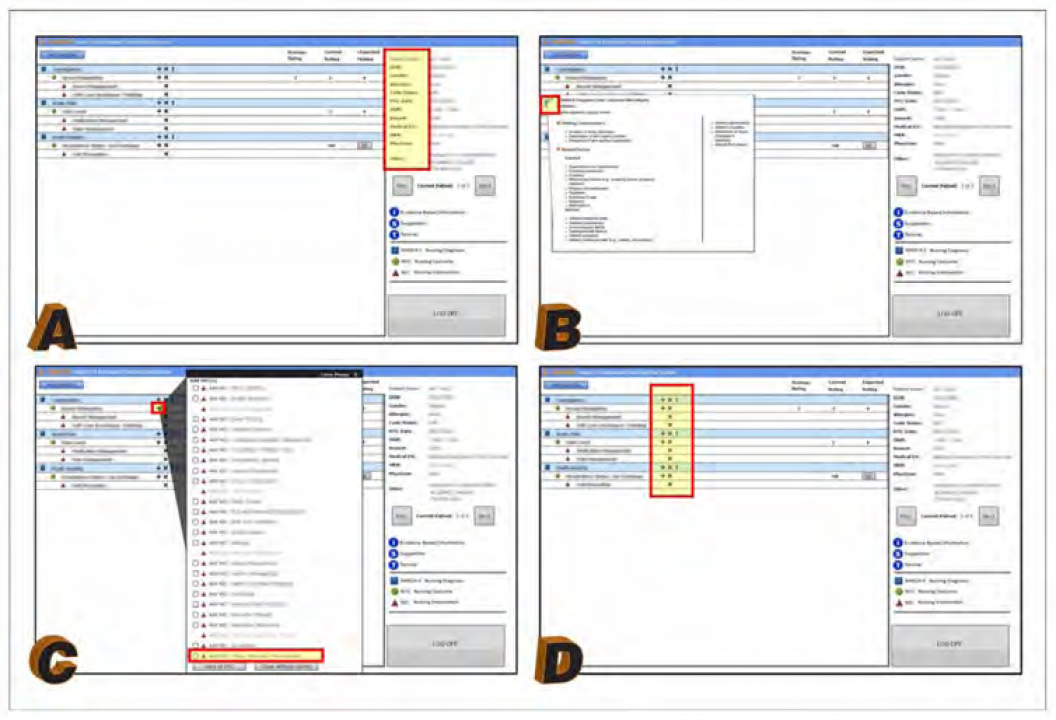
Authors: Stifter, J., Sousa, V., Febretti, A., Dunn Lopez, K., Johnson, A., Yao, Y., Keenan, G., Wilkie, D. J.
Publication: International Journal for Nursing Knowledge, vol 29, no 4, pp. 242–252 To determine acceptability, usefulness, and ease of use for four nursing clinical decision support interface prototypes. In a simulated hospital environment, 60 registered nurses (48 female; mean age=33.7 10.8; mean years of experience=8.1 9.7) participated in a randomized study with four study groups. Measures included acceptability, usefulness, and ease of use scales. Mean scores were high for acceptability, usefulness, and the ease of use for all four groups. Inexperienced participants (<1 year) reported higher perceived ease of use (p=.05) and perceived usefulness (p=.01) than those with ≥1 year experience. Participants completed the protocol and reported that all four interfaces, including the control (HANDS), were acceptable, easy to use, and useful. Further study is warranted before clinical implementation within the electronic health record. Keywords: clinical decision support; practice-based evidence; electronic health record; end-of-life care; interface usability; simulation Date: September 1, 2017 Document: View PDF |