|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Predicting late symptoms of head and neck cancer treatment using LSTM and patient reported outcomes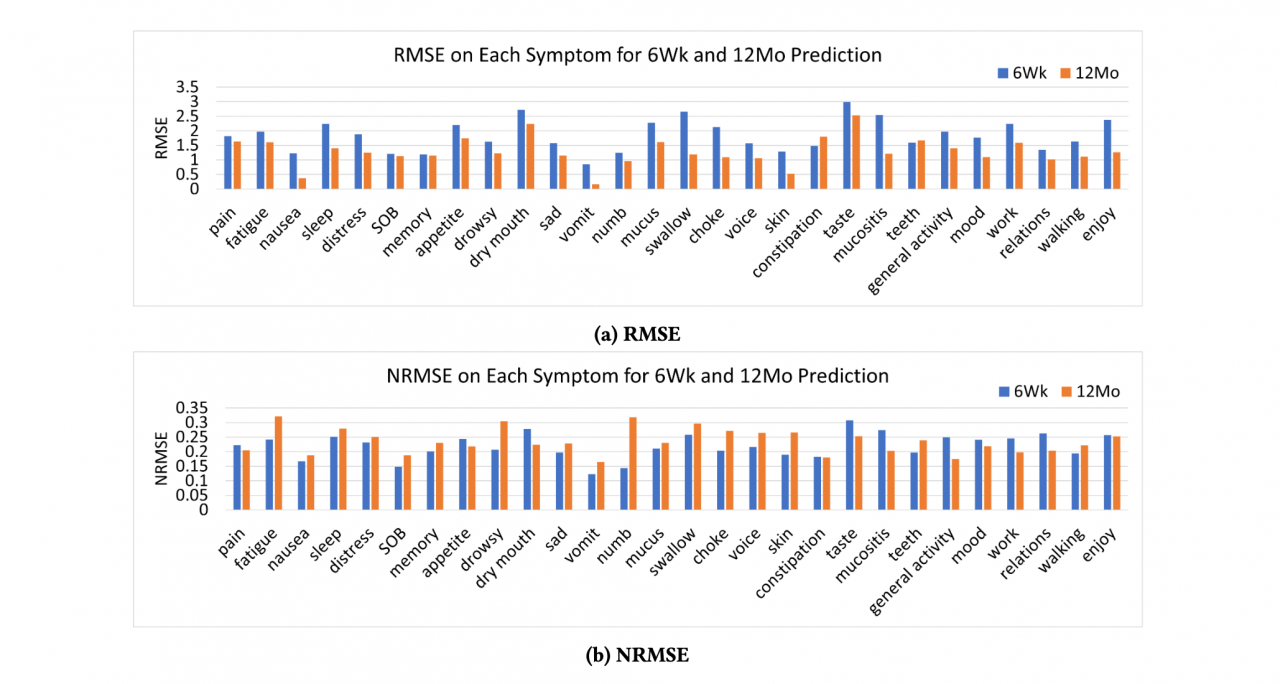
Authors: Wang, Y., Canahuate, G., Van Dijk, L., Mohamed, A.S.R., Fuller, C.D., Zhang, X., Marai, G.E.
Publication: 25th International Database Engineering & Applications Symposium (IDEAS 2021), Montreal, QC, Canada, pp. 273–279 URL: https://doi.org/10.1145/3472163.3472177 Patient-Reported Outcome (PRO) surveys are used to monitor patients’ symptoms during and after cancer treatment. Late symptoms refer to those experienced after treatment. While most patients experience severe symptoms during treatment, these usually subside in the late stage. However, for some patients, late toxicities persist negatively affecting the patient’s quality of life (QoL). In the case of head and neck cancer patients, PRO surveys are recorded every week during the patient’s visit to the clinic and at different follow-up times after the treatment has concluded. In this paper, we model the PRO data as a time-series and apply Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) neural networks for predicting symptom severity in the late stage. The PRO data used in this project corresponds to MD Anderson Symptom Inventory (MDASI) questionnaires collected from head and neck cancer patients treated at the MD Anderson Cancer Center. We show that the LSTM model is effective in predicting symptom ratings under the RMSE and NRMSE metrics. Our experiments show that the LSTM model also outperforms other machine learning models and time-series prediction models for these data. CCS Concepts: Computing methodologies; Neural networks Date: July 14, 2021 - July 16, 2021 Document: View PDF |