|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Multi-Organ Spatial Stratification of 3-D Dose Distributions Improves Risk Prediction of Long-Term Self-Reported Severe Symptoms in Oropharyngeal Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy: Development of a Pre-Treatment Decision Support Tool.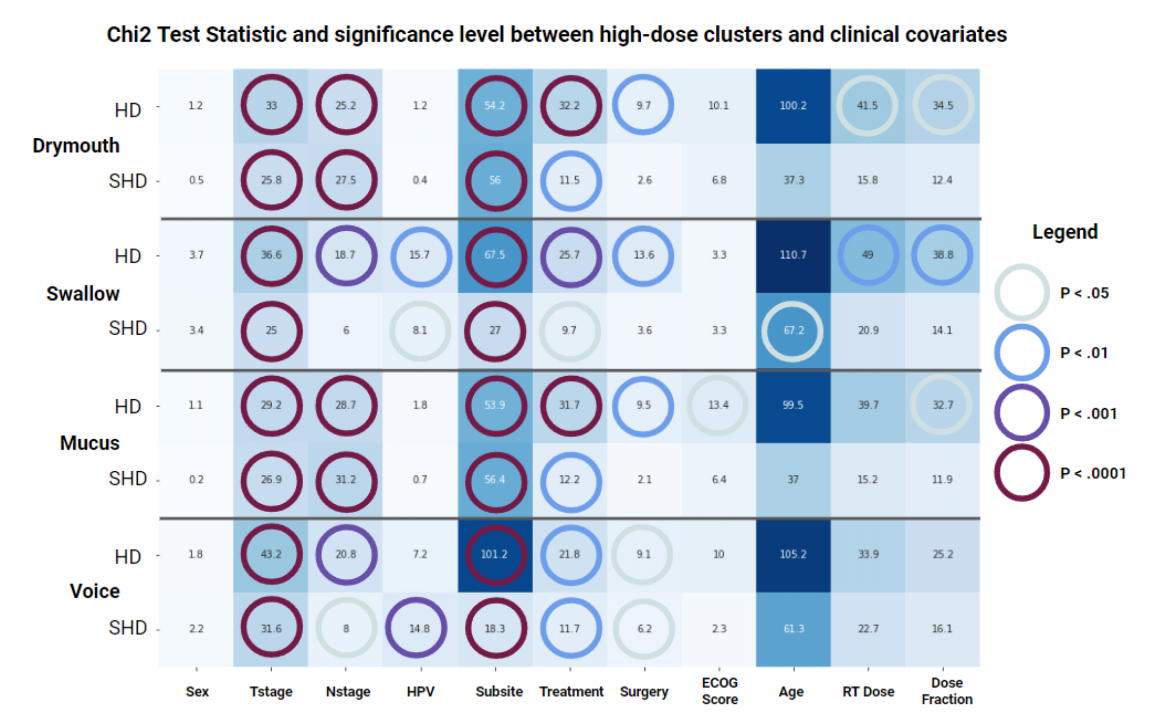
Authors: Wentzel, A., Mohamed, A.S.R., Naser, M.A., Van Dijk, L.V., Hutcheson, K., Moreno, A.M., Fuller, C.D., Canahuate, G., Marai, G.E.
Publication: Frontiers in Oncology URL: https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1210087 Recent advances in precision medicine for treating Oropharyngeal cancer (OPC) have led to significant improvements in survival for patients. However, OPC survivors often are left with severe side effects that result from damage to vital tissues in the head and neck caused by secondary radiation received during treatment. These side effects can persist for months after treatment cessation, and diminish the patients’ quality of life. Existing guidelines for radiation therapy plans identify dose limits to individual organs with the goal to avoid or minimize permanent tissue damage and their related toxicity. However, existing tools fail to account for either the three-dimensional nature of dose distributions or the fact that critical organs often work as a system that can have multiple failure points. We present an unsupervised approach for stratifying patients based on three-dimensional dose distributions to multiple organs and evaluate their association with long-term patient-reported symptoms. We apply this method to predicting severe patient-reported symptoms 6 months after ceasing radiation therapy for OPC patients. For actionable interpretability, we introduce a rule-mining method that simplifies our strata into a set of dose thresholds, and demonstrate that these thresholds outperform existing dose treatment guidelines. Keywords: Radiation therapy; Oropharynx cancer; Head and Neck cancer; Stratification; Symptom Burden; Quality of Life Date: July 17, 2023 Document: View PDF |