|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Mapping the walk: A scalable computer vision approach for generating sidewalk network datasets from aerial imagery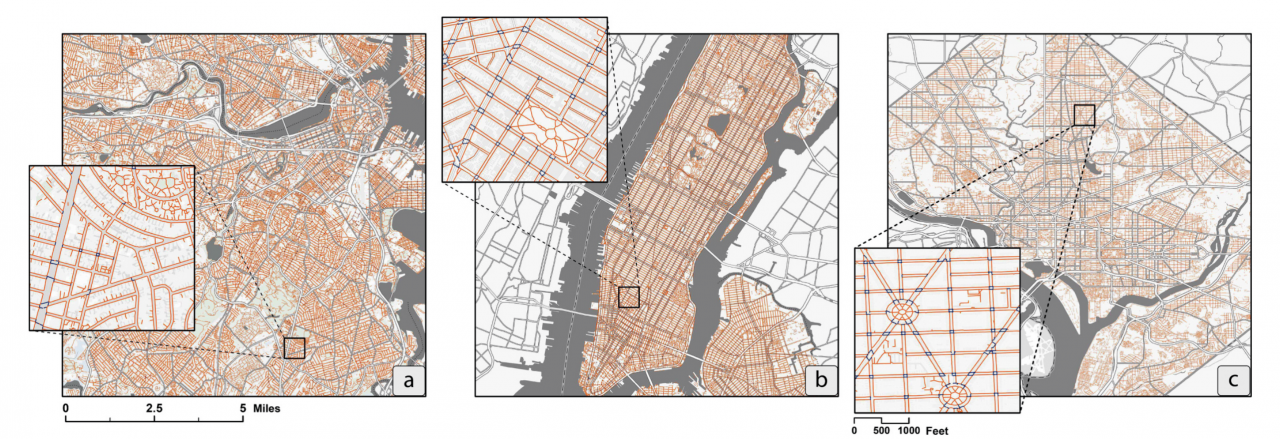
Authors: Hosseini, M., Sevtsuk, A., Miranda, F., Cesar, R.M., Silva, C.T.
Publication: Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, vol 101, no 10195, Elsevier Ltd. URL: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2023.101950 While cities around the world are increasingly promoting streets and public spaces that prioritize pedestrians over vehicles, significant data gaps have made pedestrian mapping, analysis, and modeling challenging to carry out. Most cities, even in industrialized economies, still lack information about the location and connectivity of their sidewalks, making it difficult to implement research on pedestrian infrastructure and holding the technology industry back from developing accurate, location-based Apps for pedestrians, wheelchair users, street vendors, and other sidewalk users. To address this gap, we have designed and implemented an end-to-end open-source tool - TILE2NET - for extracting sidewalk, crosswalk, and footpath polygons from orthorectified aerial imagery using semantic segmentation. The segmentation model, trained on aerial imagery from Cambridge, MA, Washington DC, and New York City, offers the first open-source scene classification model for pedestrian infrastructure from sub-meter resolution aerial tiles, which can be used to generate planimetric sidewalk data in North American cities. TILE2NET also generates pedestrian networks from the resulting polygons, which can be used to prepare datasets for pedestrian routing applications. The work offers a low-cost and scalable data collection methodology for systematically generating sidewalk network datasets, where orthorectified aerial imagery is available, contributing to over-due efforts to equalize data opportunities for pedestrians, particularly in cities that lack the resources necessary to collect such data using more conventional methods. Keywords: Pedestrian network extraction, Semantic segmentation, Automated network generation, Pedestrian infrastructure Date: February 22, 2023 Document: View PDF |