|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Kiviat Defense: An Empirical Evaluation of Visual Encoding Effectiveness in Multivariate Data Similarity Detection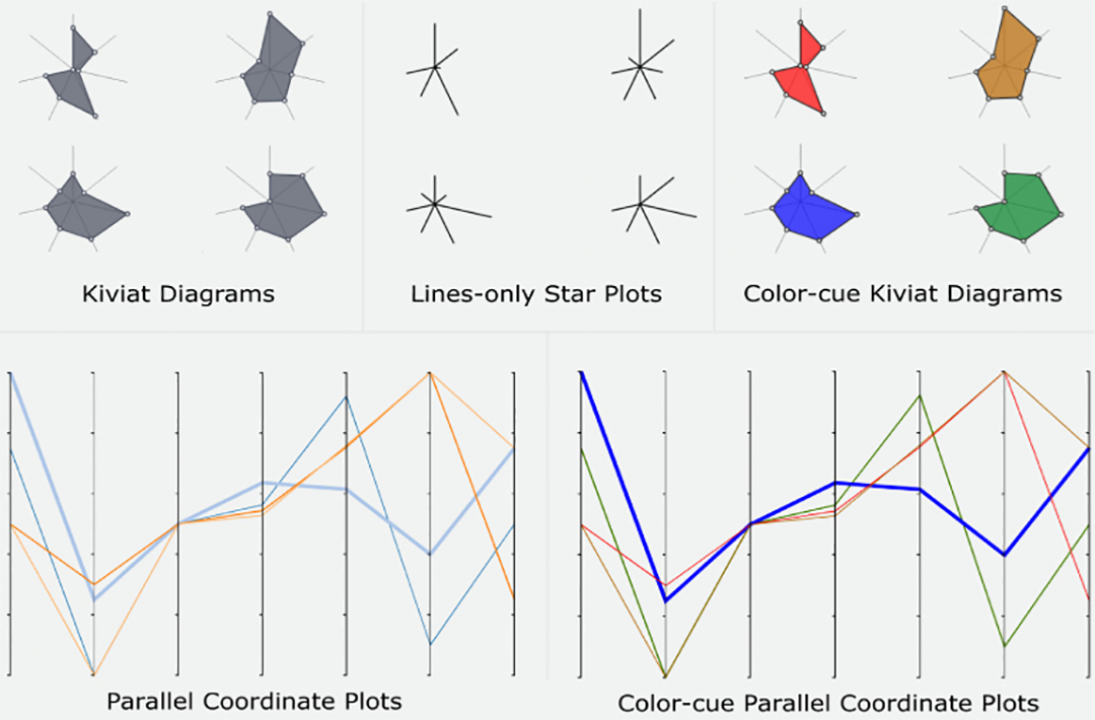
Authors: Mantovani, M., Wentzel, A., Trelles Trabucco, J., Michaelis, J., Marai, G.E.
Publication: Journal of Imaging Science and Technology, Society for Imaging Science and Technology, no 6040, Electronic Imaging 2024, Burlingame, CA, pp. 1-13 URL: https://doi.org/10.2352/J.ImagingSci.Technol.2023.67.6.060406 Similarity detection seeks to identify similar, but distinct items over multivariate datasets. Often, similarity cannot be defined computationally, leading to a need for visual analysis, such as in cases with ensemble, computational, patient cohort, or geospatial data. In this work, we empirically evaluate the effectiveness of common visual encodings for multivariate data in the context of visual similarity detection. We conducted a user study with 40 participants to measure similarity detection performance and response time under moderate scale (16 items) and large scale (36 items). Our analysis shows that there are significant differences in performance between encodings, especially as the number of items increases. Surprisingly, we found that juxtaposed star plots outperformed superposed parallel coordinate plots. Furthermore, color-cues significantly improved response time, and attenuated error at larger scales. In contrast to existing guidelines, we found that filled star plots (Kiviats) outperformed other encodings in terms of scalability and error. Date: January 22, 2024 - January 25, 2024 Document: View PDF |